· For example, rotational kinetic energy is the energy possessed by a body which is moving in circles, eg planets revolving around the sun have rotational kinetic energy;The kinetic energy K of a planet is ½mv², where v is the planet's tangential velocity The total energy E which is of interest is KV A planet also has rotational kinetic energy that is not included The energy E is the amount of energy that would be required to remove a planet from our solar system The notation (nEm) stands for n×10 mThe two equations agree when the average translational kinetic energy of the molecules is K av = (3/2)kT Here we have a fundamental connection between temperature and the average translational kinetic energy of the atoms they are directly proportional to one another Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the atoms

Kinetic Energy Definition Formula Britannica
What are five examples of kinetic energy
What are five examples of kinetic energy-Photon with energy of 01 MeV (million electron volts) or larger is also often referred to as a gamma ray An MeV is an energy unit, equal to the kinetic energy an electron would gain by being accelerated through a voltage difference of 1 MV (10 6 volts) Photons whose energy is in the range of 01 to 100 keV are usuallyWhen you use the equation Eg = mgh, the only condition on h is that it must be measured in a straight line F A car with mass moving with a speed of 4n has the same kinetic energy as a car of mass 16 m moving with a speed of 2n F When energy changes from one form to another absolutely no energy is lost T




Kinetic Energy Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
The kinetic particle theory explains the properties of solids, liquids and gases There are energy changes when changes in state occur Brownian motion is the random movement of fluid particles · An observable is a dynamic variable of a system that can be experimentally measured (eg, position, momentum and kinetic energy) In systems governed by classical mechanics, it is a realvalued function (never complex), however, in quantum physics, every observable in quantum mechanics is represented by an independent operator that is used to obtain physical information · kinetic friction = 75 N Q2 A car is moving at a uniform speed with the normal force of 1000 N If the kinetic friction applied on this car is 500 N Then compute the coefficient of the kinetic friction involved here?
Vibrational kinetic energy is the energy possessed by an object due to vibration, eg vibrating phone has a vibrational kinetic energy;By Steven Holzner When an object falls, its gravitational potential energy is changed to kinetic energy You can use this relationship to calculate the speed of the object's descent Gravitational potential energy for a mass m at height h near the surface of the Earth is mgh more than the potential energy would be at height 0Learn about kinetic and gravitational potential energy Struggling to get your head round revision or exams?
Kinetic energy is defined as the energy that is produced by an object due to its motion When an object is set to acceleration, there is a definite need to apply certain forces The application of force needs work, and after the work is done, the energy gets transferred to the object making it move at a constant velocity · The kinetic energy, K, is defined as the energy stored in an object because of its motion An object in motion has the ability to do work and thus can be said to have energy It is called kinetic energy, from the Greek word kinetikos, meaning "motion" The kinetic energy depends on the speed of an object and is the ability of a movingIn classical mechanics, kinetic energy (KE) is equal to half of an object's mass (1/2*m) multiplied by the velocity squared For example, if a an object with a mass of 10 kg (m = 10 kg) is moving at a velocity of 5 meters per second (v = 5 m/s), the kinetic energy is



Everyday Motion




Potential Energy Potential And Kinetic Energy Siyavula
The kinetic energy of an object mathematically can be written as Kinetic Energy = 1/2 m v 2 Where, m = mass of an object v = velocity of an object Kinetic energy is a scalar quantity, ie, it has only magnitude but no direction The standard unit of kinetic energy is joule (J), and the imperial unit of kinetic energy is the footpound(ftlb)The kinetic energy equation is KE=05 mv^2 where m=mass and v=velocity/speed The potential energy equation is PE=mgh , where m=mass, g= acceleration due to gravity and h=height Transferability Kinetic energy can be transferred from one object to another as is the case with what happens during collisionsKinetic energy is transferred between objects and can be transformed into other forms of energy YoYo is a great example to describe the transformation of kinetic energy While beginning to play with it, one starts by letting it rest in the hand, at this point, all the energy is stored in the ball in the form of potential energy




5 Examples Of Kinetic Energy In Everyday Life



What Are Some Examples Of Kinetic Friction Quora
Answer Known Normal force \(F_n = 1000 N\), Kinetic friction\( F_k = 500 N\), Formula for, the coefficient of kinetic energy isPotential energy also includes other forms The energy stored between the plates of a charged capacitor is electrical potential energy What is commonly known as chemical energy, the capacity of a substance to do work or to evolve heat by undergoing a change of composition, may be regarded as potential energy resulting from the mutual forces among its molecules and atomsTranslational kinetic energy is the energy possessed by an object moving from one point to another Translational kinetic energy



Internal Energy Example



13 Examples Of Kinetic Energy In Everyday Life Studiousguy
During the collision of small objects, kinetic energy is first converted to potential energy associated with a repulsive or attractive force between the particles (when the particles move against this force, ie the angle between the force and the relative velocity is obtuse), then this potential energy is converted back to kinetic energy (when the particles move with this force,• The kinetic energy due to the transitional motion of a mol of gas molecules is equal to (3/2) RT Pressure of the Gas • Consider N molecules of an ideal gas, in a cubic container of side L (m) • A typical molecule has mass m (kg), and velocity u (u x, u y, u z) (ms · contentThis energy topic deals with motion energy, thermal energy, gravitational potential energy, and elastic potential energy and ideas about energy transformations, energy transfer, and conservation of energy The ideas presented here are based on the Energy Transformations map in Atlas of Science Literacy, Volume 2 (AAAS



What Are Some Examples Of Kinetic And Potential Energy Quora



Mechanical Energy
Kinetic energy refers to a form of energy which an object or particle has due to the motion On the application of the net force on an object, the object speeds up and consequently generates this energy This energy is a property of an object or particle which moves Furthermore, this energy depends not only on the motion but also on the massKinetic energy, form of energy that an object or a particle has by reason of its motion Kinetic energy is a property of a moving object or particle and depends not only on its motion but also on its mass The kind of motion may be translation, rotationEk=1/2mv² As you see from the formula, kinetic energy of the objects is only affected by the mass and velocity of the objects The unit of the Ek is again from the formula kg
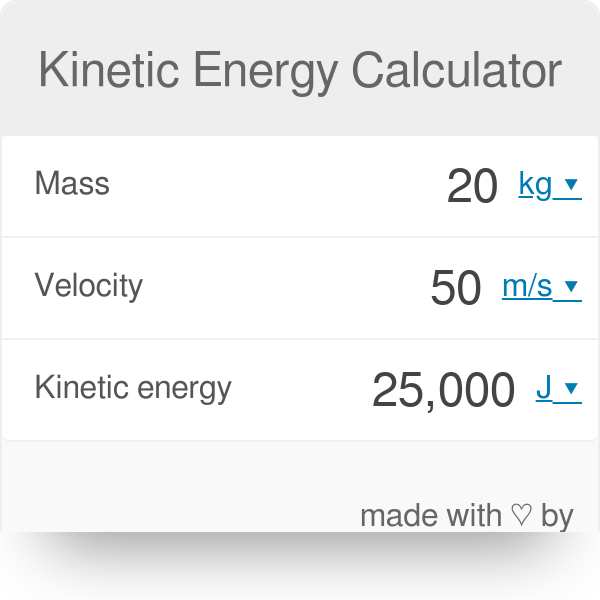



Kinetic Energy Calculator




Today Ch 7 On Energy V Note All
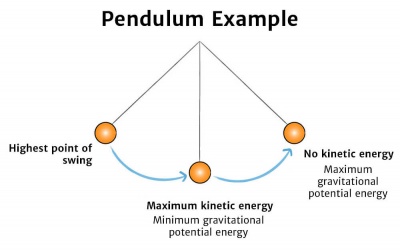
· The stage is set We started building the energy transfer model (ETM), and we've talked about the flavors of energyWe are ready for a new representation to help us start thinking about energy storage in a system In a day or two, we'll be using energy bar charts, but first, we'll get used to thinking about energy storage with a simpler, stepping stone diagram · The amount of kinetic energy (motion energy) an object has is proportional to the mass of the object and increases rapidly with increasing speed The amount of thermal energy an object has depends on the disordered motions of its atoms or molecules and the number and types of atoms or molecules of which the object is madePotential and kinetic energy This chapter builds on the basic concept of energy The chapter explains the difference between kinetic and potential energy The law of conservation of energy is also introduced Energy cannot be created or destroyed, but can be transferred from one part of the system to other parts




5 Examples Of Kinetic Energy In Everyday Life




13 Examples Of Kinetic Energy In Everyday Life Studiousguy
· If you want to calculate the energy of an object which is in motion, our kinetic energy calculator is highly recommended The potential energy formula Let's look under the hood of the potential energy calculator To help you picture it, our example will be the massive wrecking ball on a crane The gravitational potential energy of this ball · Kinetic energy definition The encyclopedia provides the following definition of kinetic energy The kinetic energy of an object is the energy that it possesses due to its motionIt is defined as the work needed to accelerate a body of a given mass from rest to its stated velocityIf the kinetic energy of the system is conserved during a collision, it is called an elastic collision (ie) The total kinetic energy before collision and after collision remains unchanged The collision between subatomic particles is generally elastic The collision between two




Kinetic And Potential Energy Proprofs Quiz




Forms Of Energy Knowledge Bank Solar Schools
PAVEMENT ENERGY HARVESTING SYSTEM TO CONVERT VEHICLES KINETIC ENERGY INTO ELECTRICITY PhD Thesis in Doctoral Program in Transport Systems supervised by Professor Adelino Ferreira, presented to the Department of Civil Engineering of the Faculty of Sciences and Technology of the University of Coimbra August 17Here are some Kinetic Energy Examples when you are walking or running your body is exhibiting kinetic energy A bicycle or skateboard in motion possesses kinetic energy Running water has kinetic energyThis energy is called kinetic energy Kinetic energy of the objects having mass m and velocity v can be calculated with the formula given below;



Potential And Kinetic Energy Ppt Video Online Download



Kinetic And Potential Energy Ppt Video Online Download
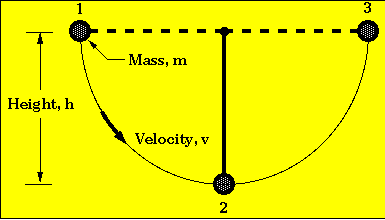
Our tips from experts and exam survivors will help you throughPotential Energy Eg A sheep of mass 47kg is slowly raised through a height of 63m Find the gain in potential energy PE = mgh = 47 x 10 x 63 = 2961J As an object falls, its potential energy is changed into kinetic energy Kinetic energy GAINED = Potential energy LOSTThe kinetic energy is equal to 1/2 the product of the mass and the square of the speed
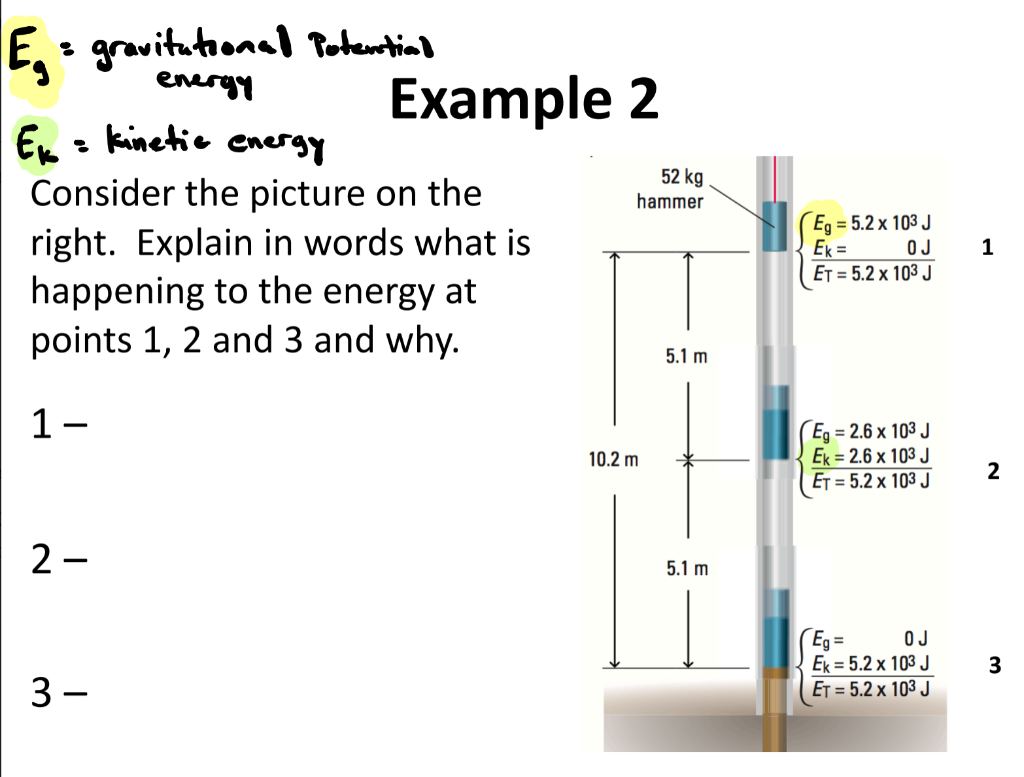



Solved 52 Kg E Gravitational Potential Energy Example 2 Chegg Com




What Is Kinetic Energy Kinetic Energy Examples
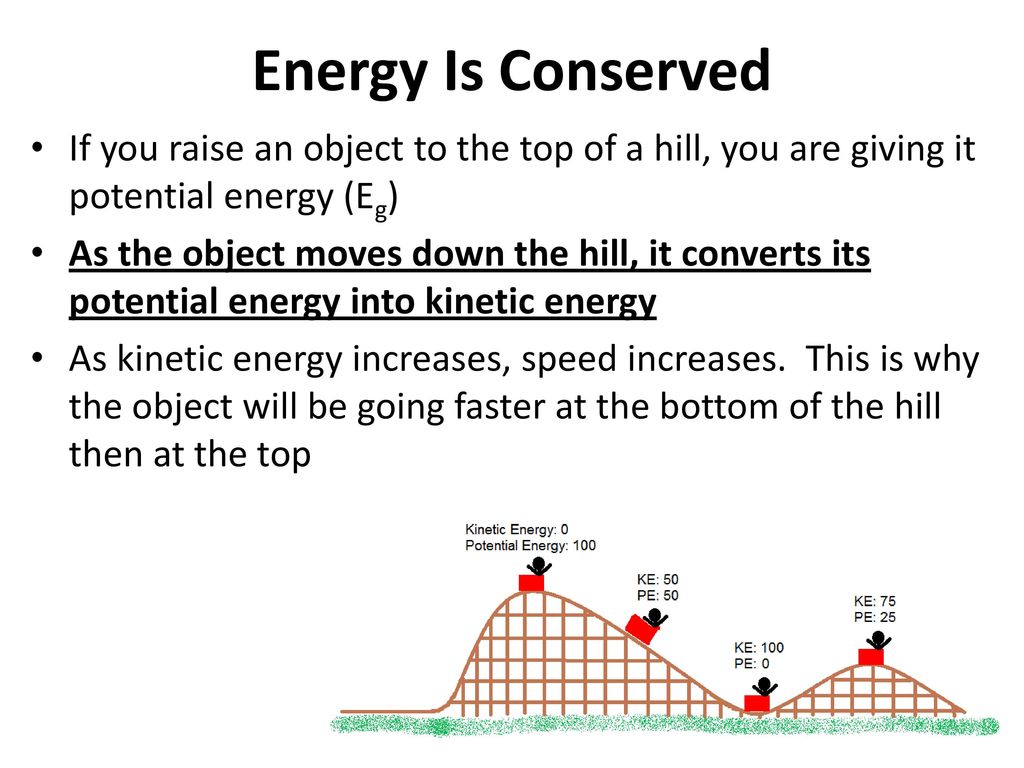
Radiant Energy Examples Radiant energy is a type of kinetic energy, referring to energy that travels by waves or particles The energy is created through electromagnetic waves and is most commonly experienced by humans in the form of heat Some examples include Incandescent light bulb When you turn on a light with a traditional incandescent light bulb, it gives off two forms of energy · What are some examples of kinetic energy?Eg top = J Ek top= 0 J Eg bottom = 115 J Ek bottom = 1/2 m (v)2 = 1/2 (51) (19)2 = 255 x 36 = 918 J This shows that as the gravitational energy decreases the kinetic energy increases So as the paint can travels in the arc, it loses gravitational energy and gains kinetic energy It will have the most kinetic energy at the bottom of




13 Examples Of Kinetic Energy In Everyday Life Studiousguy




Potential Energy Potential And Kinetic Energy Siyavula
KINETIC ENERGY Objects have energy because of their motion;Kinetic Energy Formula Kinetic energy is the energy possessed by a body due to its motion Kinetic Energy Formula is articulated as Where, mass of the body = m, the velocity with which the body is travelling is v The Kinetic energy is articulated in Kgm 2 /s 2Now that you have the kinetic energy and the gravitational energy you can find the total energy of the system Et= Eg Ek Et= 19 x10^3J 410J Et= 2310J Therefore the total energy of the system is 2310J Work A kg curling rock starts from rest and has a final velocity of 64m/s
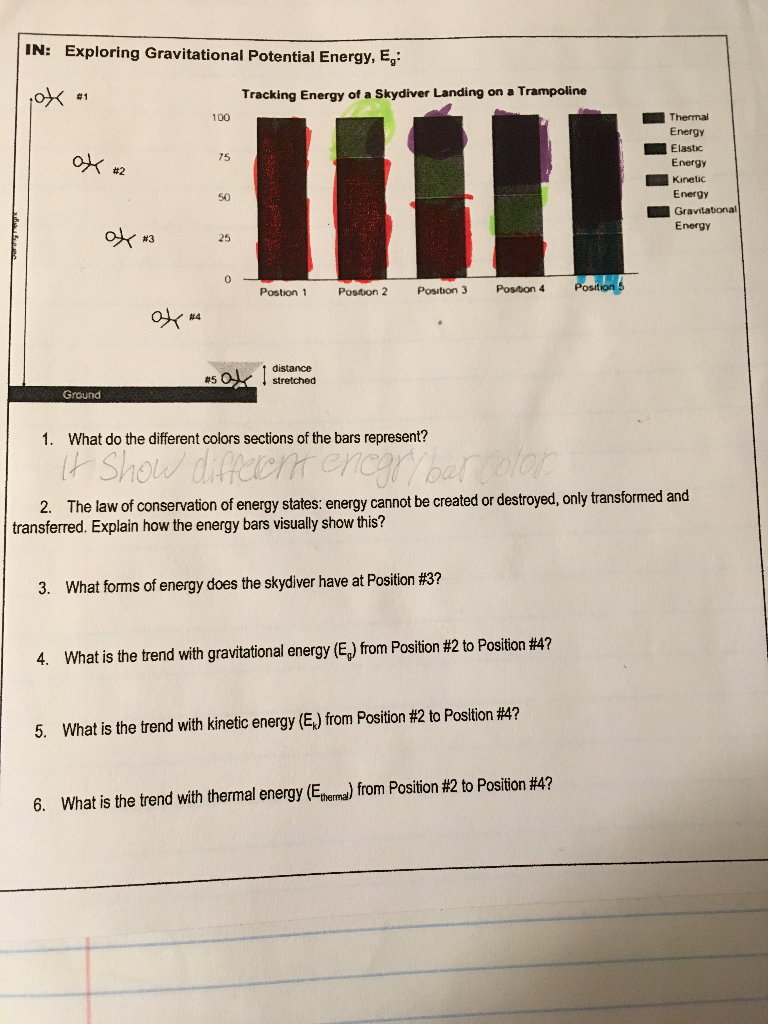



Solved 4 What Is The Trend With Gravitational Energy Eg Chegg Com
(133).jpg)



Quiz Potential And Kinetic Energy Questions Proprofs Quiz
//youtube/_DPhLrFLtbA here we wll learn what is kinetic energy AND it's formula of taking out follow me on facebook=https//wwwfacebookcom/profThe total (internal) energy in a system includes potential and kinetic energy This is contrast to external energy which is a function of the sample with respect to the outside environment (eg kinetic energy if the sample is moving or potential energy if the sample is at aExamples of Kinetic Energy 1 An airplane has a large amount of kinetic energy in flight due to its large mass and fast velocity 2




Kinetic Energy An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Potential And Kinetic Energy Example Problem Work And Energy Examples
Free online Kinetic Energy calculator with which you can calculate the energy of an object or body in motion given its mass and velocity The calculator can be used to solve for mass or velocity given the other two Supports multiple metrics like meters per second (m/s), km per hour, miles per hour, yards and feet per second Mass units in metric and imperial units · Kinetic energy (KE) is the energy of a body in motion, which means it's essentially the energy of all moving objects It is one of the two main forms of energy, along with potential energy, which is the stored energy contained within objects at rest · 14 Kinetic energy is a vector quantity FALSE 15 The gravitational potential energy of a moving object is always zero FALSE 16 When mechanical energy is conserved, the kinetic energy you end up with always equals the gravitational potential energy you start with FALSE 17 A force acting perpendicular to an object's displacement does negative work



Potential Energy Knowledge Bank Solar Schools




Kinetic Energy What Is Kinetic Energy In Simple Words Kinetic Energy And Potential Energy Youtube
· The internal energy of a system is identified with the random, disordered motion of molecules;Egg Drop Assignment 3My apparatus' gravitational potential energy, Eg, is turned into kinetic energy, which is the energy held by moving things, just like any other falling item Because of air resistance, not all of the potential energy became kinetic energy 4 Using a lighter device can increase your egg's chances of surviving the drop, since the lighter the mass, the less force it will079 Kinetic Energy In this video Paul Andersen explains how the kinetic energy of an object if due to the motion of an object Objects can have kinetic en
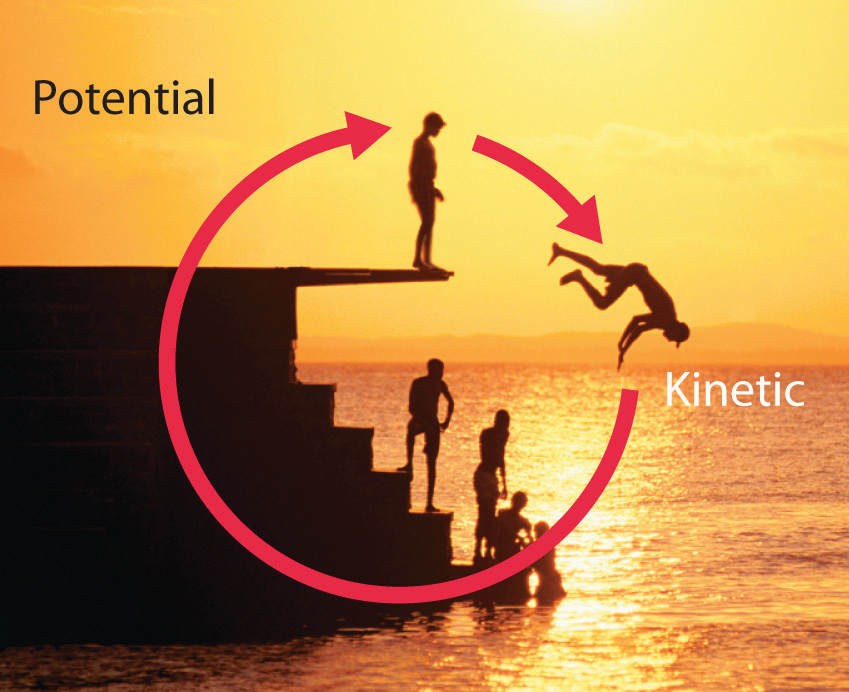




Energy And Work
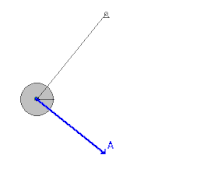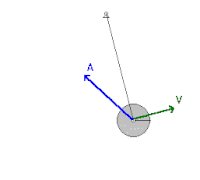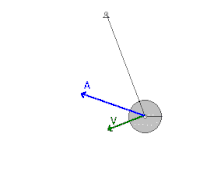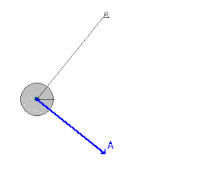



Mechanical Energy Wikipedia
Few Examples of Kinetic Energy The following are typical examples of kinetic energy A wrecking ball used to demolish a building through utilization of the kinetic energy it possesses in motion Conversion of liquid water to steam, by virtue of the fast movement of



What Are Some Examples Of Kinetic And Potential Energy Quora




Energy Flow In The Cell What Is Energy Capacity To Do Work 1 Kinetic Energy Energy Of Movement E G Light Heat Electricity Movement Of Large Objects 2 Potential Energy Stored Energy E
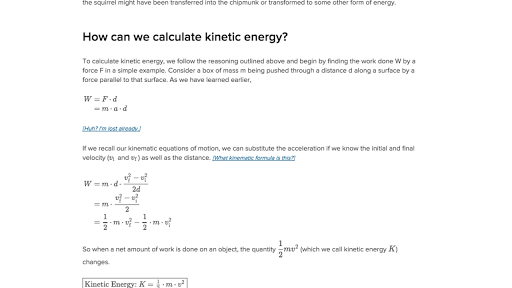



What Is Kinetic Energy Article Khan Academy




How To Calculate Kinetic Energy 9 Steps With Pictures Wikihow



Kinetic Gravitational Potential Energy Ppt Download



Matsc 101 Energy Fundamentals 3




Solved Problem 2 Kinetic Energy Of A Rolling Hollow Spher Chegg Com




Kinetic Energy Wikipedia




10 Best Examples Of Kinetic Energy Rankred




Potential Energy Definition Examples Facts Britannica




How To Calculate Kinetic Energy 9 Steps With Pictures Wikihow




What Is Kinetic Energy Live Science



Internal Energy Example
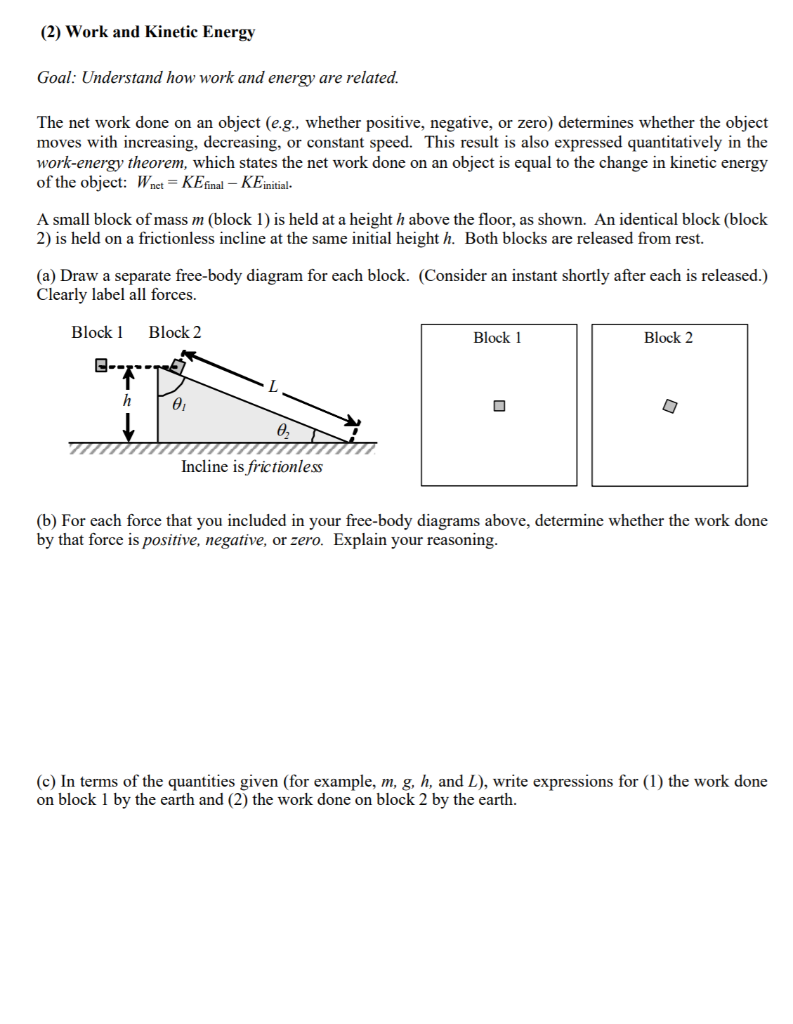



Solved 2 Work And Kinetic Energy Goal Understand How W Chegg Com




Examples Of Kinetic Energy What Are They Access2knowledge Org




Energy And States Of Matter Ppt Video Online Download




Kinetic Energy Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock




Kinetic Energy Pictures




Study Guide For Science Standard 6 2 New



Gravitational Energy Knowledge Bank Solar Schools




Examples Of Kinetic Energy



12 Examples Of Potential Energy In Everyday Life Studiousguy




10 Best Examples Of Kinetic Energy Rankred




10 Examples Of Mechanical Energy In Everyday Life Studiousguy




Potential Energy Examples Examples Of Potential Energy Potential Energy Physics Youtube




What Are Some Examples Of Kinetic And Potential Energy Quora




Potential And Kinetic Energy Aumsum Kids Science Education Children Youtube




What Is Chemical Energy Definition And Examples




Kinetic Energy Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock




What Is Kinetic Energy Definition Formula Examples Unit Types




13 Examples Of Kinetic Energy In Everyday Life Studiousguy




Kinetic And Potential Energy Of Motion Lesson Teachengineering
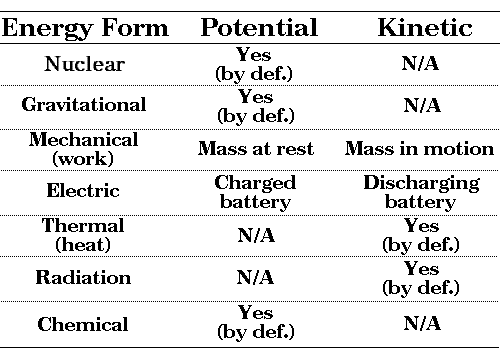



Matsc 101 Energy Fundamentals 3




Do Now Q1 Give 1 Example Of Kinetic Energy Ppt Video Online Download
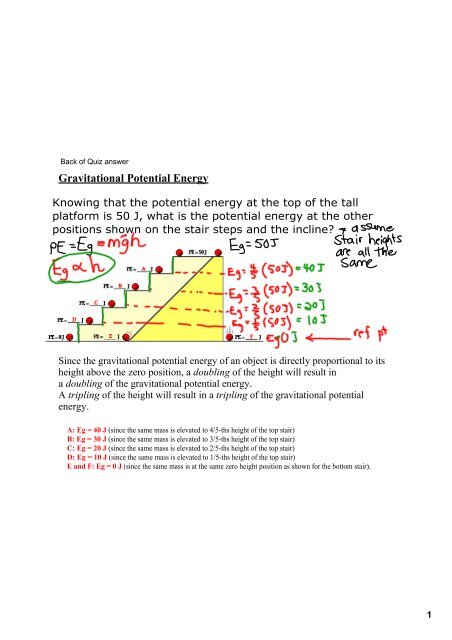



Day 04 Kinetic Energy




How To Calculate Kinetic Energy 9 Steps With Pictures Wikihow
.png)



Quiz Potential And Kinetic Energy Questions Proprofs Quiz




Comparison Of The Kinetic Energy With The Internal Energy E G The Download Scientific Diagram




13 Examples Of Kinetic Energy In Everyday Life Studiousguy




Potential And Kinetic Energy Ppt Video Online Download




What Are Some Examples Of Kinetic And Potential Energy Quora




Kinetic Energy Definition Formula Britannica




Kinetic Energy Example Problems Youtube




Potential Energy Potential And Kinetic Energy Siyavula
/main-energy-forms-and-examples-609254-v3-5b562a0cc9e77c0037514831.png)



10 Types Of Energy And Examples
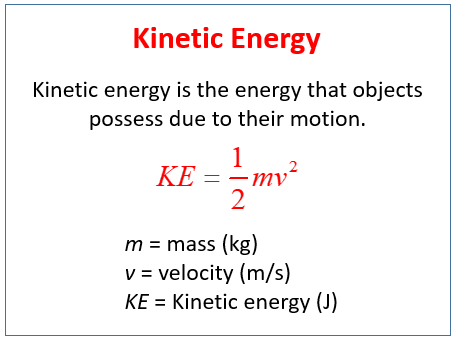



Kinetic Energy Examples Video Lessons Examples Step By Step Solutions




Which One Is An Example Of Kinetic Energy Brainly Com




Kinetic Energy To Potential Energy Relationship In Different Energy Types Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



The Law Of Conservation Of Energy
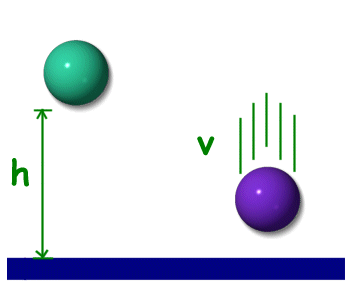



Physics For Kids Potential Energy



Mechanical Energy




Conservation Of Energy Video Khan Academy




Global Distributions Of Mean Energies And Strain Rate A Geostrophic Download Scientific Diagram




Kinetic Energy Definition Formula Examples Teachoo




Kinetic Energy Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock




Examples Of Kinetic Energy What Are They Access2knowledge Org
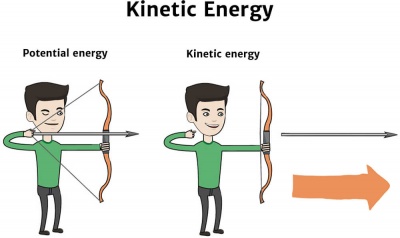



Kinetic Energy Knowledge Bank Solar Schools




Potential Energy Definition Examples Facts Britannica




Work And Energy




Kinetic And Potential Energy Ppt Video Online Download
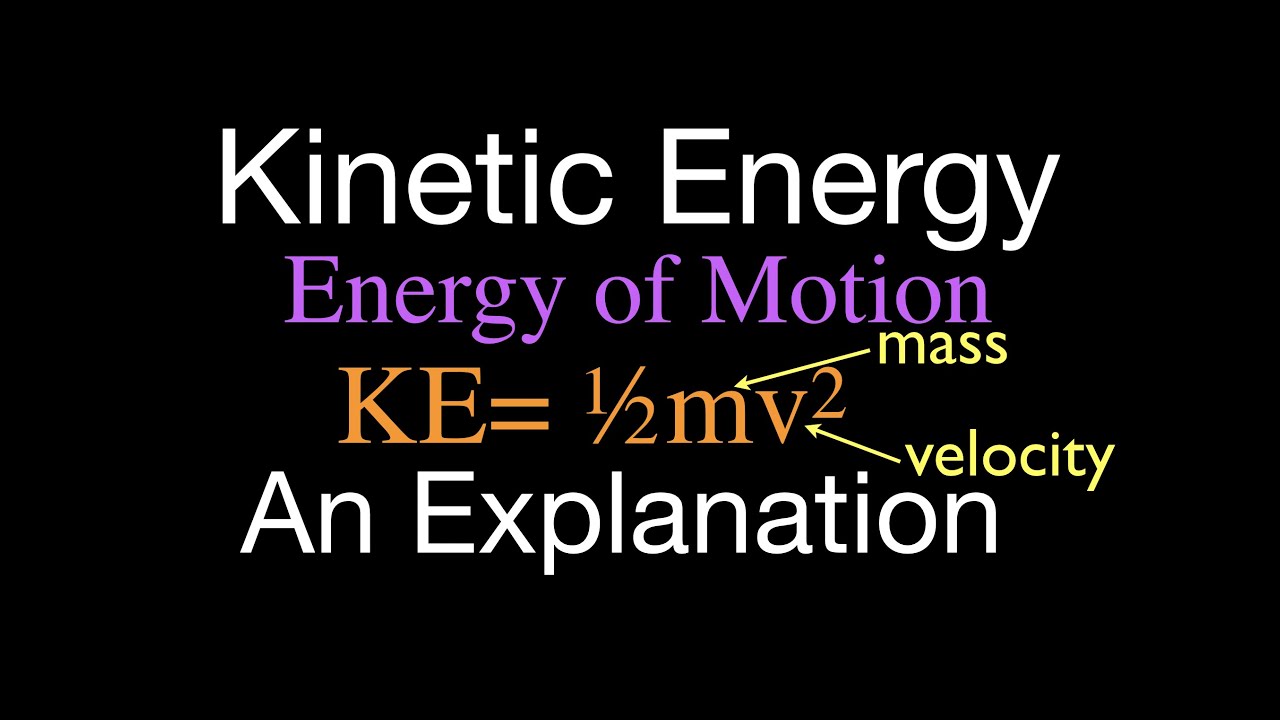



Kinetic Energy Example Problems Youtube
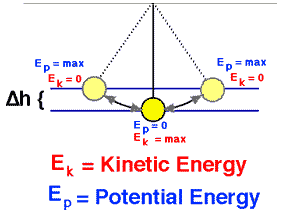



What Is Example Of Mechanical Energy Definition




10 Examples Of Mechanical Energy In Everyday Life Studiousguy




Gravitational And Potential Energy And Kinetic Energy Lesson




What Are Some Examples Of Kinetic And Potential Energy Quora




5 Examples Of Kinetic Energy In Everyday Life




Tj Potential Energy Is The Stored Or Pent Up Energy Of An Object Potential Energy Is Ofte Work Energy And Power Potential Energy Kinetic And Potential Energy



Energy Formulas




Potential And Kinetic Energy Explained




Kinetic And Potential Energy Diagrams Diagram Quizlet




Solved 1 Gravitational Potential Energy Eg Mgh Find The Chegg Com



Task A 2 Lesson Plan



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿